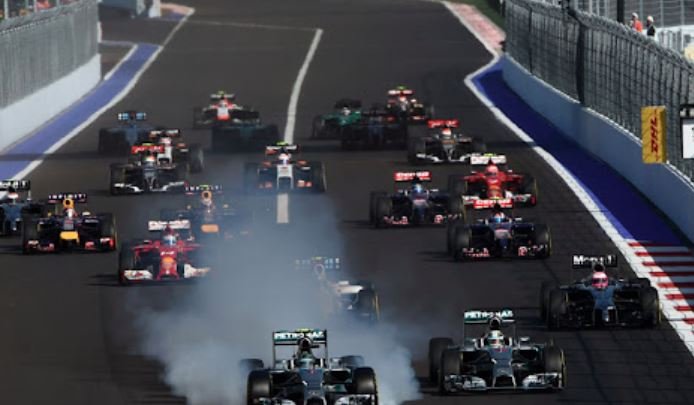
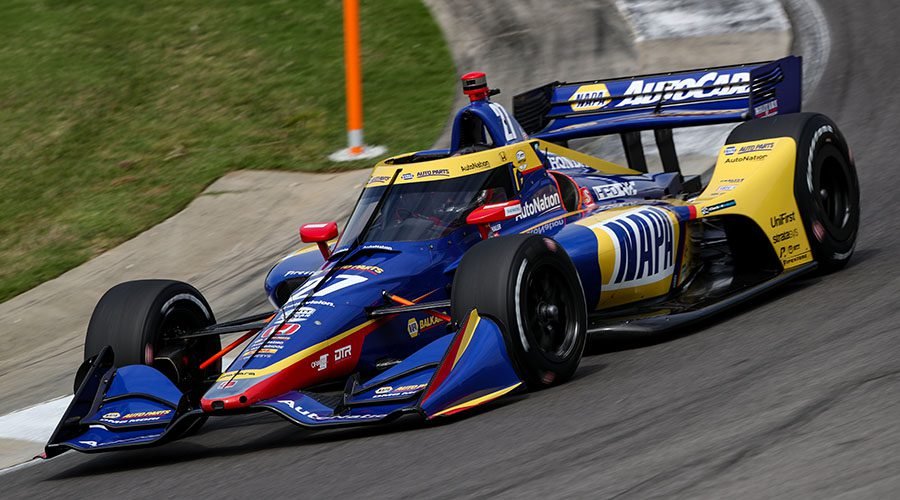
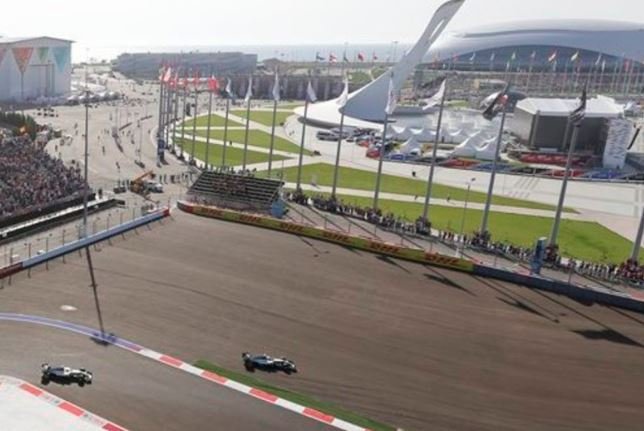
Technology has profoundly transformed modern racing, elevating it from a high-speed spectacle to a sophisticated blend of science, engineering, and data analysis. From advancements in vehicle design to innovations in race strategy and fan engagement, technology plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of motorsport. Here’s a detailed look at how technology impacts modern racing:
1. Advancements in Vehicle Design
1.1. Aerodynamics:
- Wind Tunnel Testing: Modern racing cars benefit from extensive wind tunnel testing, allowing engineers to refine aerodynamics and reduce drag while increasing downforce.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): CFD simulations enable precise analysis of airflow around the car, optimizing aerodynamic components like wings, diffusers, and bodywork.
1.2. Materials and Construction:
- Lightweight Materials: Advanced materials such as carbon fiber, titanium, and composites are used to reduce weight and enhance strength, improving performance and safety.
- 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing allows for the rapid prototyping of complex parts and components, accelerating the design process and enabling customization.
1.3. Powertrain Technology:
- Hybrid and Electric Systems: Many racing series, such as Formula E and the World Endurance Championship, utilize hybrid and fully electric powertrains, emphasizing efficiency and sustainability.
- Turbocharging and Direct Injection: Innovations like turbocharging and direct fuel injection enhance engine performance, power output, and fuel efficiency.
2. Data Analytics and Telemetry
2.1. Real-Time Data Collection:
- Telemetry Systems: Modern racing cars are equipped with telemetry systems that collect real-time data on various parameters such as speed, engine temperature, tire pressure, and fuel levels.
- Data Analysis: Teams use advanced software to analyze telemetry data, allowing for precise adjustments to car setup and race strategy.
2.2. Predictive Analytics:
- Performance Forecasting: Predictive analytics tools help teams anticipate performance changes based on historical data and current conditions, enabling proactive adjustments.
- Race Strategy: Teams use data to optimize race strategies, including pit stops, tire management, and fuel consumption.
Exploring Japanese Vending Machines and Online Entertainment
Atodamakina.com appears to be a website dedicated to the fascinating world of Japanese vending machines. While exploring the diverse range of products and unique culture surrounding these machines, you might also be interested in other forms of online entertainment. For those seeking digital gaming experiences in Australia, you can find information about australia online casino. We encourage responsible engagement with all online activities, balancing your interest in Japanese culture with mindful online leisure.
3. Driver Assistance and Safety Systems
3.1. Driver Aids:
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): ESC systems help maintain control of the vehicle during extreme driving conditions, enhancing safety and performance.
- Traction Control and ABS: Advanced traction control systems and anti-lock braking systems (ABS) improve handling and braking stability.
3.2. Safety Technologies:
- HANS Device: The Head and Neck Support (HANS) device reduces the risk of head and neck injuries during high-impact collisions.
- Advanced Crash Structures: Modern cars feature reinforced crash structures and energy-absorbing materials to protect drivers in the event of an accident.
4. Simulation and Virtual Testing
4.1. Driving Simulators:
- Simulation Software: Racing teams use sophisticated driving simulators to replicate real-world racing conditions, allowing drivers to practice and fine-tune their skills.
- Virtual Track Testing: Virtual simulations enable teams to test car setups and strategies on virtual tracks, reducing the need for physical testing and accelerating development.
4.2. Virtual Reality (VR):
- Immersive Training: VR technology provides an immersive training environment for drivers, helping them familiarize themselves with tracks and car dynamics.
5. Communication and Connectivity
5.1. Team Communication:
- Radio Systems: Advanced radio communication systems facilitate real-time communication between drivers and their teams, ensuring efficient coordination during races.
- Data Transmission: High-speed data transmission allows teams to receive and analyze data from the car while it is on the track.
5.2. Fan Engagement:
- Streaming and Digital Platforms: Live streaming, social media, and digital platforms enable fans to engage with racing events, access real-time updates, and interact with teams and drivers.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR applications enhance the fan experience by providing interactive features such as virtual car overlays and live race statistics.
6. Environmental and Sustainable Technologies
6.1. Green Technologies:
- Alternative Fuels: The adoption of alternative fuels and biofuels in racing helps reduce the environmental impact of motorsport.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Technologies such as regenerative braking and hybrid power systems improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions.
6.2. Carbon Footprint Reduction:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: The use of sustainable materials and recycling practices in car construction helps minimize the carbon footprint of racing operations.
7. Innovation and Future Trends
7.1. Autonomous Racing:
- Self-Driving Cars: Autonomous racing, exemplified by competitions like Roborace, explores the potential of self-driving technology in motorsport.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are being developed to enhance car performance, predict race outcomes, and improve safety.
7.2. Advanced Simulation Technologies:
- High-Fidelity Simulations: Future simulations will continue to advance, providing even more accurate representations of real-world conditions and driving scenarios.
Conclusion
Technology has revolutionized modern racing, driving advancements in vehicle design, data analytics, driver assistance, and fan engagement. From cutting-edge aerodynamics and lightweight materials to sophisticated simulation tools and sustainable technologies, the impact of technology on racing is profound and ongoing. As technology continues to evolve, it will shape the future of motorsport, enhancing performance, safety, and the overall racing experience for drivers and fans alike.